Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It requires ongoing management to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life. One of the key components of managing diabetes effectively is regular monitoring through blood tests. These tests provide crucial information about how well diabetes is being controlled and help detect potential complications early. This blog post will explore the routine blood tests that diabetics need, what to expect during these tests, and why they are essential for managing the condition.
1) The Basics of Diabetes and Blood Tests
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels. There are three main types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A condition where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin.
- Gestational Diabetes: A type that develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
Blood tests are crucial for diagnosing diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels, and assessing the risk of complications. Regular blood tests help diabetics and their healthcare providers understand how well the treatment plan is working and make necessary adjustments.
2) Common Routine Blood Tests for Diabetics
HbA1c Test
- What it measures: The average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Why it’s important: This test is a key indicator of long-term glucose control. An HbA1c level below 7% is generally considered good control for most diabetics, though individual targets may vary.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test
- What it measures: Blood glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Why it’s important: It helps diagnose diabetes and monitor how well fasting glucose levels are being managed. A fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or higher indicates diabetes.
Postprandial Blood Sugar Test
- What it measures: Blood glucose levels after eating, typically two hours post-meal.
- Why it’s important: It assesses how food impacts blood sugar levels, helping to adjust diet and medications accordingly. A postprandial blood sugar level of less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) is generally the target for diabetics.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- What it measures: Blood glucose levels before and after consuming a glucose-rich drink.
- Why it’s important: It is used to diagnose gestational diabetes and can also help diagnose type 2 diabetes. A 2-hour blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher indicates diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test
- What it measures: Blood glucose levels at any given time, regardless of when you last ate.
- Why it’s important: It provides a snapshot of current glucose levels and is useful for monitoring glucose control throughout the day. A random blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes.
Lipid Profile
- What it measures: Levels of cholesterol (HDL, LDL) and triglycerides.
- Why it’s important: Diabetics are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. A lipid profile helps identify risk factors and guide treatment to manage cholesterol levels.
Kidney Function Tests
- What they measure: Levels of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in the blood.
- Why they’re important: Diabetes can lead to kidney damage. These tests help detect early signs of kidney disease, allowing for timely intervention.
3) Testing for Diabetes at Home: Is It Good or Not?
Home testing for diabetes has become increasingly popular and accessible, offering several advantages and some limitations.
Overview of Home Testing Options
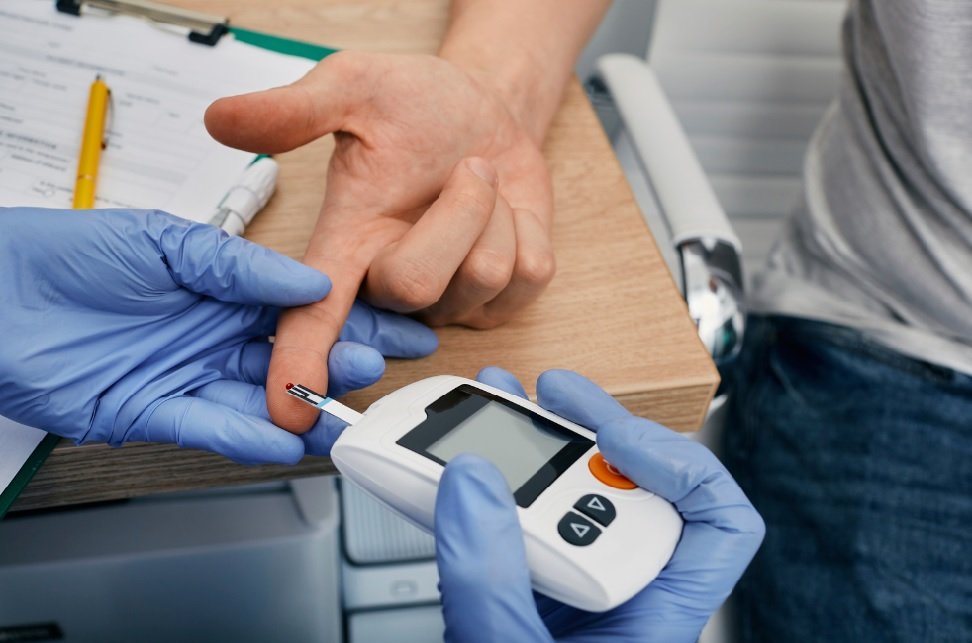
- Glucometers: Devices that measure blood glucose levels using a small blood sample from a finger prick.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Devices that measure glucose levels in real-time through a sensor placed under the skin.
- Home Testing Kits: Over-the-counter kits that can measure blood sugar levels but cannot diagnose diabetes.
Benefits of Home Testing
- Convenience: Allows for frequent monitoring without frequent visits to a healthcare provider.
- Immediate Feedback: Helps in making real-time decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Better Day-to-Day Management: Empowers diabetics to manage their condition more proactively.
Limitations and Concerns
- Accuracy Issues: Home devices may not always be as accurate as lab tests.
- Potential for Misinterpretation: Without proper guidance, there’s a risk of misinterpreting the results, leading to inappropriate adjustments in treatment.
- Diagnostic Limitations: Home testing kits and blood glucose meters cannot diagnose diabetes; they only show blood sugar levels at the moment of testing.
- Importance of Professional Guidance: Regular consultation with healthcare providers is essential to ensure that home testing is done correctly and the data is interpreted appropriately.
Tips for Effective Home Testing
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
- Keep a detailed log of readings, noting any factors that might affect blood sugar levels (e.g., meals, exercise).
- Share your readings with your healthcare provider during regular check-ups.
4) Preparing for Blood Tests
Proper preparation can help ensure accurate blood test results and a smoother testing experience.
General Guidelines for Fasting or Non-Fasting Tests
- Fasting Tests: Do not eat or drink anything except water for 8-12 hours before the test.
- Non-Fasting Tests: No special preparation is needed, but follow any specific instructions from your healthcare provider.
Tips for Reducing Anxiety Before Blood Tests
- Stay hydrated.
- Practice deep breathing or relaxation techniques.
- Bring a friend or family member for support.
- Inform the phlebotomist if you have a fear of needles.
Importance of Accurate Medical History and Medication List
- Provide a complete and accurate medical history to your healthcare provider.
- List all medications, supplements, and over-the-counter drugs you are taking, as some can affect blood test results.
5) Frequency of Blood Tests for Diabetics
The frequency of blood tests varies depending on individual needs, type of diabetes, and overall health.
Recommended Frequency of Different Blood Tests
- HbA1c Test: Every 3-6 months.
- Fasting and Postprandial Blood Sugar Tests: Daily or as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Lipid Profile: At least once a year.
- Kidney Function Tests: At least once a year or more frequently if there are signs of kidney disease.
Factors That May Require More Frequent Testing
- Changes in medication or treatment plans.
- Experiencing symptoms of high or low blood sugar.
- Pregnancy or planning for pregnancy.
- Signs of complications or other health issues.
6) The Role of Blood Tests in Preventing Complications
Regular blood tests play a crucial role in preventing diabetes-related complications.
Detecting and Preventing Complications
- Neuropathy: Regular blood sugar monitoring helps prevent nerve damage.
- Retinopathy: Early detection through blood tests and regular eye exams can prevent vision loss.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Monitoring cholesterol and blood pressure helps reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney Disease: Kidney function tests can detect early signs of damage, allowing for timely intervention.
Importance of Early Detection and Proactive Management
- Regular testing allows for the early detection of potential issues, enabling prompt treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
- Proactive management reduces the risk of serious complications and improves overall health and quality of life.
7) Advances in Blood Testing Technology
Technological advancements have revolutionized blood glucose monitoring, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
New Technologies and Methods
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Provide real-time glucose readings and alerts for high or low levels.
- At-Home Test Kits: Allow for comprehensive testing of various health markers from the comfort of home.
Benefits of Technological Advancements
- Improved Accuracy: More precise readings help in better diabetes management.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly devices encourage consistent monitoring.
- Data Integration: Many devices can sync with smartphones and apps, providing comprehensive data analysis and easy sharing with healthcare providers.
FAQ’s
Why is a lipid profile important for diabetics?
A lipid profile measures cholesterol (HDL, LDL) and triglyceride levels, helping to assess cardiovascular risk, which is higher in individuals with diabetes.
What does the HbA1c test measure?
The HbA1c test measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, providing a snapshot of long-term glucose control.
Can you test for diabetes at home?
Yes, you can test for diabetes at home using glucometers or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs). These devices measure blood glucose levels from a small sample obtained through a finger prick or sensor, providing immediate results for monitoring purposes.
How to use diabetic test strips?
Diabetic test strips are used with glucometers to measure blood glucose levels. Simply insert the test strip into the meter, prick your finger to draw a small blood sample, apply the blood to the strip, and wait for the meter to display your glucose level.
Is fasting required for diabetes blood tests?
Yes, fasting is required for some diabetes blood tests, such as fasting blood sugar tests. This involves refraining from eating or drinking (except water) for 8-12 hours prior to the test to obtain accurate glucose readings.
Conclusion:
Regular blood tests are indispensable for individuals managing diabetes, providing vital insights into their health status and helping to prevent complications. From monitoring blood glucose levels with tests like HbA1c, fasting and postprandial tests, to assessing lipid profiles and kidney function, these tests enable healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively. Whether performed at a healthcare facility or through convenient home testing options like glucometers or continuous glucose monitors, accurate and timely results are crucial for proactive diabetes management.
For reliable and professional blood tests, contact Akshar Imaging Centre, Ahmedabad ensuring thorough pathology lab services to support your diabetes care. By staying proactive with routine tests and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of complications and achieve better health outcomes. Take charge of your diabetes management today with informed testing and personalized care.
